Over-Fed and Under-Nourished:
As a society, we are in unprecedented times when though food is in abundance and readily available for consumption, nutritional value that we gain from food is poorer than ever. As a result we have become a society of overfed and undernourished people. Over 65% Americans are obese or overweight and over 80% lack in one or more nutritional elements. Below are the most common nutritional deficiencies, associated complications and solutions.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is the sunshine vitamin and due to its extensive involvement in maintaining metabolism and facilitating epigenetic expression of over 1000 genes, it is considered by many as a hormone. a and we get it from direct exposure to sunlight, food and supplements.
Causes of Vitamin D deficiency:
-
Lack of sun exposure - Approximately an hour of direct sunlight exposure to normally bare skin can provide with enough vitamin D. Because we do not get enough exposure and many people need to avoid excessive sun exposure due to risks associated with skin cancers, most of us lack this source.
-
Dietary deficiency - Though we do not meet our daily dose of sunlight, we still can get enough vitamin D from healthy dietary sources. Common sources are
-
Animal sources include - Fish such as salmon, tuna, sardines, beef liver, egg yolks etc.
-
Plant sources include - Mushrooms contain vitamin D2 which still has to be converted to vitamin D3 with the help of sunlight. Wild mushrooms are much richer in its vitamin D content than regular farm grown mushrooms.
-
Fortified foods include - Cow's milk, soy milk and all other plant based milk alternatives, cereals, orange juice etc. Each of these provide about 10-15% daily requirement for vitamin D per serving.
-
-
Inflammation - Any type of inflammation in the body can lead to vitamin D deficiency. This is because much higher quantities of Vitamin D are consumed under stressful or inflamed conditions.
Complications associated with Vitamin D deficiency:
Vitamin D deficiency leads to countless complications. Some of these include,
-
Osteoporosis and Osteopenia - Vitamin D deficiency causes weak bones and increased risk of fracture.
-
Joint pains - Body and joint aches and pains are often associated with vitamin D deficiency.
-
Fatigue - Patients with vitamin D deficiency report high levels of unexplained fatigue.
-
Propensity to recurrent infections - Vitamin D deficiency leads to high risk of infections including flu, respiratory illnesses and various viral infections.
-
Chronic inflammatory conditions - Several chronic inflammatory conditions are associated with vitamin D deficiency. These include,
-
Cardiovascular disease - atherosclerosis, erectile dysfunction
-
Diabetes and additional metabolic disorders
-
Chronic lung conditions
-
Systemic lupus and additional autoimmune diseases
-
several types of arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis
-
Neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis, dementia
-
Psychiatric conditions such as depression, schizophrenia and many more.
-
Treatment and monitoring of Vitamin D deficiency:
Strategies to prevent and correct vitamin D deficiency
-
Eat a healthy and balanced diet. Look above for sources.
-
Get enough sun exposure if possible.
-
Supplement if necessary. Generally 800-1000 IU of vitamin D3 are needed / day. Under periods of stress or with borderline insufficiency, 2000 IU of vitamin D3 should be taken.
-
If you have been diagnosed with low vitamin D levels, follow the protocol below


What is missing from this full plate?
Nutrition is missing in the form of
1. Healthy fats such as omega 3
2. Healthy vitamins such as Vitamin D
3. Healthy minerals such as magnesium
4. Unsung hero (fiber)
5. and many other things
A:
Q:
A lot of Calories but no Nutrition
Magnesium
Magnesium is a mineral with a fundamental role for the health of our entire body. It in involved in over 300 metabolic processes and a disorder of the optimal level of magnesium in the body can have a variety of symptoms. Below is some information about this key nutrient.
Risk factors for magnesium deficiency:
An unhealthy lifestyle including a diet which consists of hyper-processed foods and low in vegetables and greens can lead to an acute lack of magnesium.
Other risk factors for hypomagnesemia are:
-
Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption
-
Stress
-
Lack of rest
-
Gastrointestinal disorders - Celiac disease, Crohn’s disease
-
Kidney diseases
-
Liver disorders
-
Pancreatitis
-
Diabetes
-
Use of purgatives, diuretics and laxatives
Symptoms and complications associated with Magnesium deficiency:
-
Fatigue, exhaustion despite enough rest,
-
Fainting;
-
Anxiety, depression;
-
Nervousness, irritability;
-
Muscle cramps, tremors, spasms;
-
Headaches;
-
Palpitations, arrhythmia;
-
High blood pressure;
-
Breathing difficulties;
-
Loss of appetite, nausea;
-
Constipation
Treatment of Magnesium deficiency:
First step is diagnosis. Based upon symptoms and signs, a blood test can diagnose the deficiency. If serum magnesium levels are low, following can be done to correct the deficiency. generally, 300-400 mg/day is needed for optimal metabolic functions.
-
Adopt a plant based diet containing green leafy vegetables, nuts, legumes, whole grains and dark chocolate
-
If dietary sources are not sufficient, start a magnesium supplement. Some of the formulations with specific indications include the following. The dose for each is 200-400 mg/day



-
Magnesium citrate - GI symptoms such as constipation, nausea, bloating
-
Magnesium L-threonate - Memory support, anxiety and depression
-
Magnesium glycinate - Sleep disturbances
-
Magnesium oxide - Migraines prevention
-
Magnesium malate - Widespread pain such as in fibromyalgia
-
Magnesium taurate - Glucose and blood pressure control
-
Magnesium orotate - Cardiovascular support
-
Magnesium sulfate - Epson salt applied topically for sore muscles
Omega 3 Fatty Acids
Omega 3 fats are to the brain what amino acids or proteins are to muscles.
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids belong to the family of unsaturated fatty acids that have a double carbon bond in the omega-3 position, that is, after the third carbon atom, counting from the methyl end of the fatty acid chain.
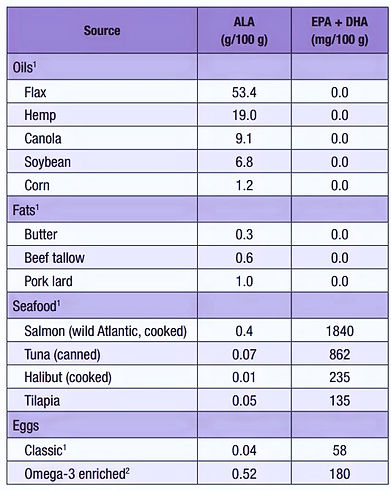
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are part of cell membranes and blood vessels, are not synthesized in the right amounts in the human body and are one of the necessary components of a full healthy diet. The main source of omega-3 is fish.
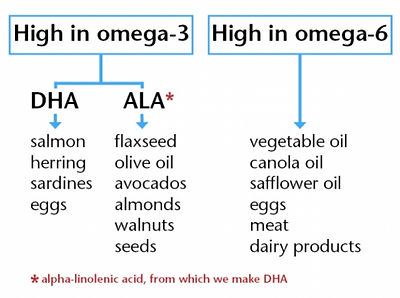
The omega-3 family includes:
-
ALA| alpha-linolenic acid,
-
EPA | eicosapentaenoic acid,
-
DHA | docosahexaenoic acid.
Health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are among the world’s most comprehensively studied nutrients. They have been shown to have powerful health benefits on the following conditions:
-
Lipid Panel - Omega-3 supplements can significantly lower blood triglycerides.
-
Inflammation and Pain - Omega 3 fats improve pain and reduce inflammation
-
Cancer- Eating foods high in omega-3 has been linked to a reduced risk of colon, prostate, and breast cancers.
-
Fatty liver- Taking omega-3 fatty acid supplements can help get rid of excess fat from your liver.
-
Depression and anxiety. Taking omega-3 supplements, such as fish oil, can help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
-
ADHD - In children with ADHD, omega-3 supplements can significantly improve various symptoms.
-
Dementia - Some studies link a higher omega-3 intake to a reduced risk of Alzheimer's disease and dementia
-
Asthma - Omega-3s may help prevent asthma in children and young adults.
-
Brain development - DHA taken during pregnancy and breastfeeding can improve your baby's intelligence and eye health.
Main food sources
Get 1500 mg - 2000 mg / day
The main food sources of omega-3-unsaturated fatty acids
-
Ground flax seeds and linseed oil;
-
Chia seeds;
-
Fish:
-
oily sea fish, fish oil
-
mackerel, anchovies, sardines and herring,
-
tuna, haddock and trout
-
-
Ginger oil;
-
Mustard oil;
-
Seeds of technical hemp and its oil;
-
Spinach;
-
Seaweed;
-
Rapeseed oil.

For additional information about fiber, click here.
Fir additional information about nutritional testing, click here.


